Global ecosystem typology
Alternative site for the Global ecosystem typology with additional information for ecosystem profiles and indicative maps.
This site is maintained by jrfep
F3.4 Freshwater aquafarms
Biome: F3. Artificial wetlands biome
Contributors:
(texts)
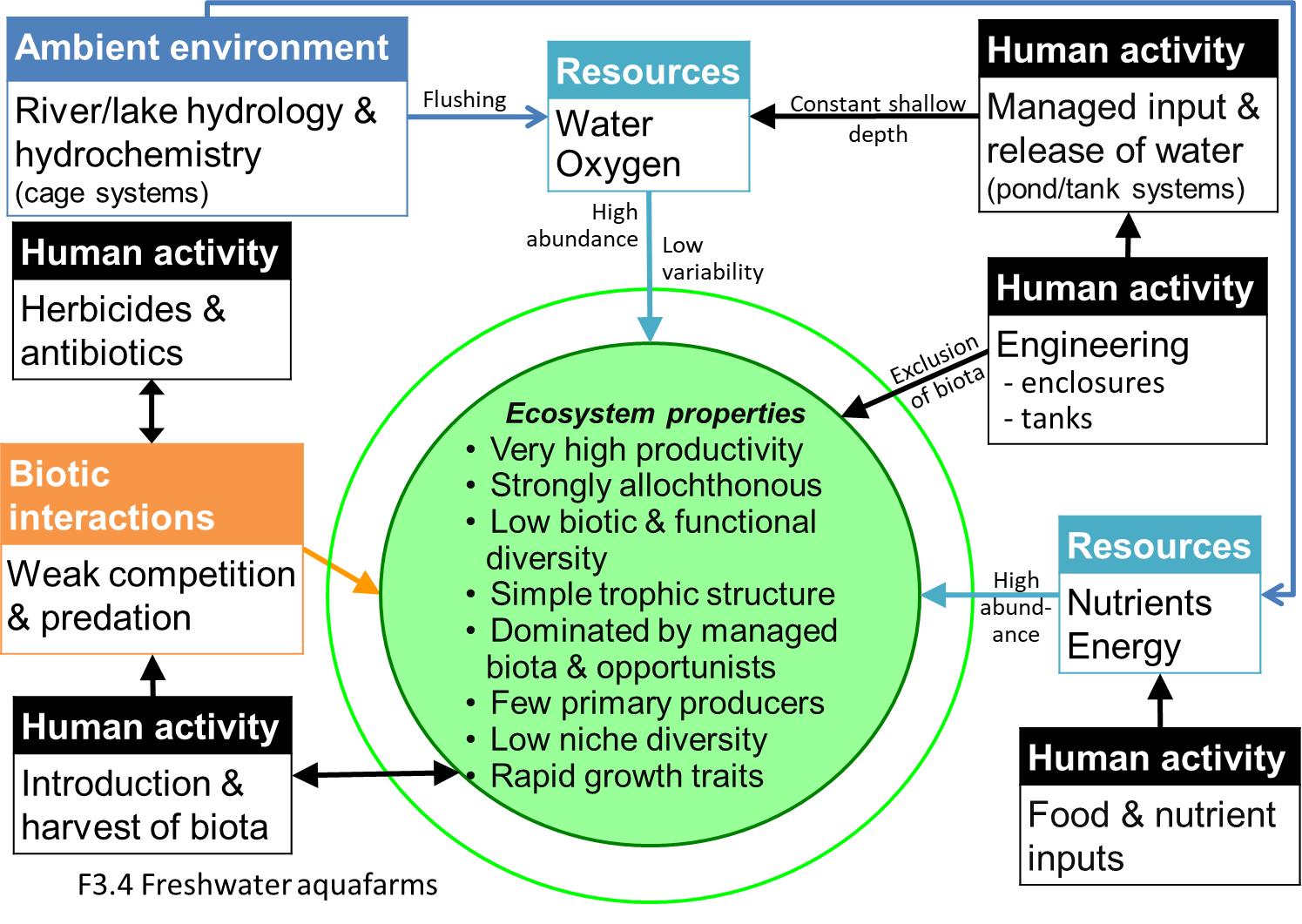
Freshwater aquafarms are ponds constructed from earthworks or cages built within freshwater lakes, rivers and reservoirs. They are most common in Asia. and used to produce species. Their commercial production of fish and crustacean involves intensive interventions, including focussed inputs of food and nutrients, and control of competitors, predators and diseases that may limit production of target species. Consequently habitat diversity and primary production are low, and non-target biota is limited to opportunistic colonisers from adjacent water sources, including insects, fish, frogs, waterbirds and some aquatic plants.
Key Features
Artificial mostly permanent waterbodies managed for production of fish or crustaceans with managed inputs of nutrients and energy Simple trophic networks of opportunistic colonists supported mainly be algal productivity.
Overview of distribution
Mostly in Asia but also in northern and western Europe, North and West Africa, the Americas, and southeast Australia and New Zealand.
Profile versions
- v1.0 (2020-01-20): RT Kingsford; DA Keith
- v2.0 (2020-05-26): RT Kingsford; M Beveridge; DA Keith
- v2.01 ():
- v2.1 (2022-04-06): RT Kingsford; M Beveridge; DA Keith Full profile available at official site
Main references
Selected references for this functional group:
Ottinger M, Clauss K, Kuenzer CJO (2016) Aquaculture: relevance, distribution, impacts and spatial assessments–a review Ocean & Coastal Management 119: 244-266 DOI:10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2015.10.015
Diagrammatic assembly model
Maps
Maps are indicative of global distribution patterns are not intended to represent fine-scale patterns. The maps show areas of the world containing major (coloured red) or minor occurrences (coloured yellow) of each ecosystem functional group. See general notes on maps.
There are 2 alternative versions of the indicative map for this functional group, please compare description and sources below.
F3.4.IM.orig_v1.0
Datasets
- FEOW-2008
Map references
Abell R, Thieme ML, Revenga C, Bryer M, Kottelat M, Bogutskaya N, Coad B, Mandrak N, Contreras Balderas S, Bussing W, Stiassny MLJ, Skelton P, Allen GR, Unmack P, Naseka A, Ng R, Sindorf N, Robertson J, Armijo E, Higgins JV, Heibel TJ, Wikramanayake E, Olson D, López HL, Reis RE, Lundberg JG, Sabaj Pérez MH, Petry P (2008) Freshwater ecoregions of the world: A new map of biogeographic units for freshwater biodiversity conservation, BioScience 58: 403–414. DOI:10.1641/B580507
F3.4.web.orig_v1.0
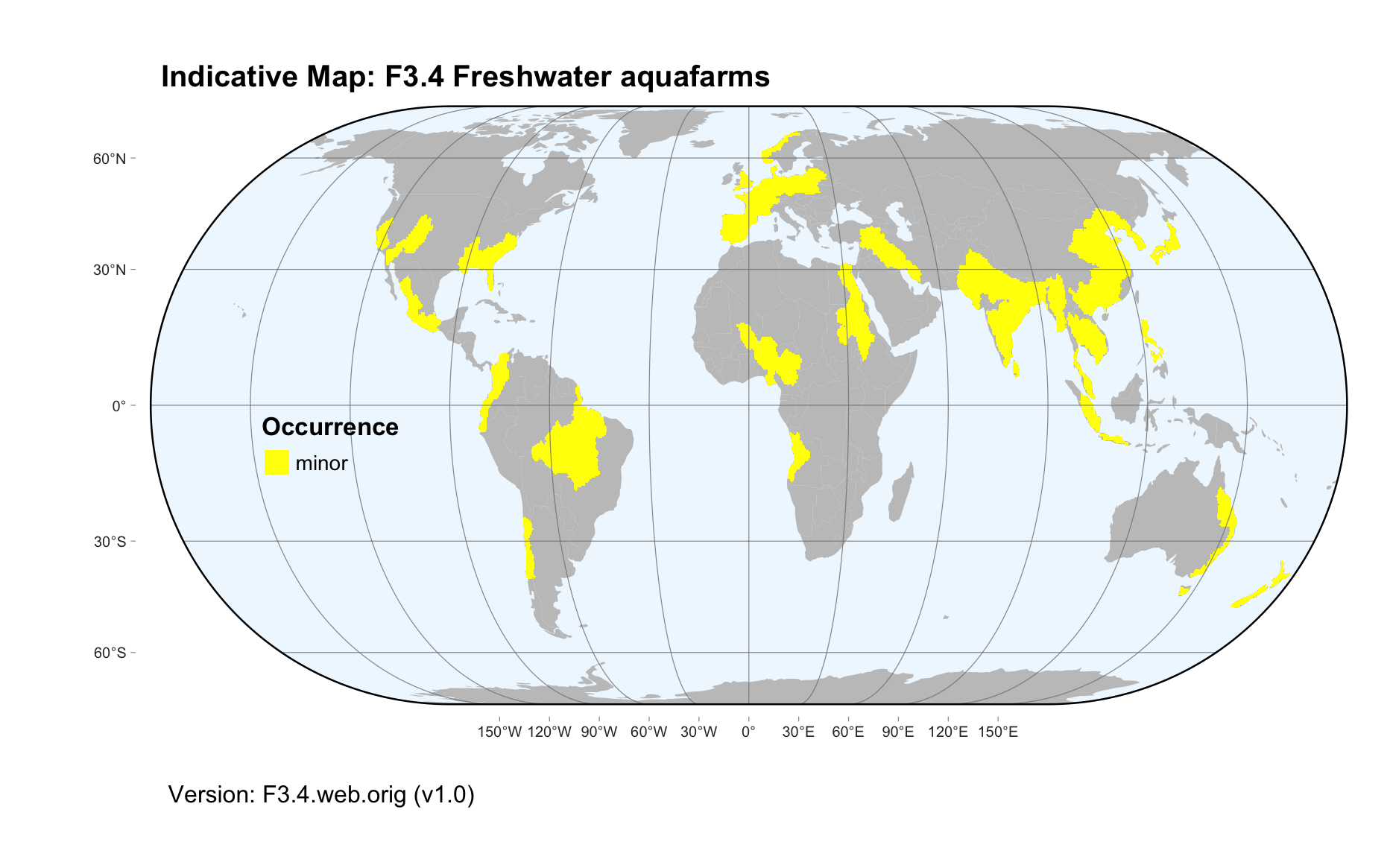
Datasets
- FEOW-2008
Map references
Abell R, Thieme ML, Revenga C, Bryer M, Kottelat M, Bogutskaya N, Coad B, Mandrak N, Contreras Balderas S, Bussing W, Stiassny MLJ, Skelton P, Allen GR, Unmack P, Naseka A, Ng R, Sindorf N, Robertson J, Armijo E, Higgins JV, Heibel TJ, Wikramanayake E, Olson D, López HL, Reis RE, Lundberg JG, Sabaj Pérez MH, Petry P (2008) Freshwater ecoregions of the world: A new map of biogeographic units for freshwater biodiversity conservation, BioScience 58: 403–414. DOI:10.1641/B580507
Check: the Glossary / Profile structure / the public document