Global ecosystem typology
Alternative site for the Global ecosystem typology with additional information for ecosystem profiles and indicative maps.
This site is maintained by jrfep
M3.1 Continental and island slopes
Biome: M3. Deep sea floors biome
Contributors:
(texts)
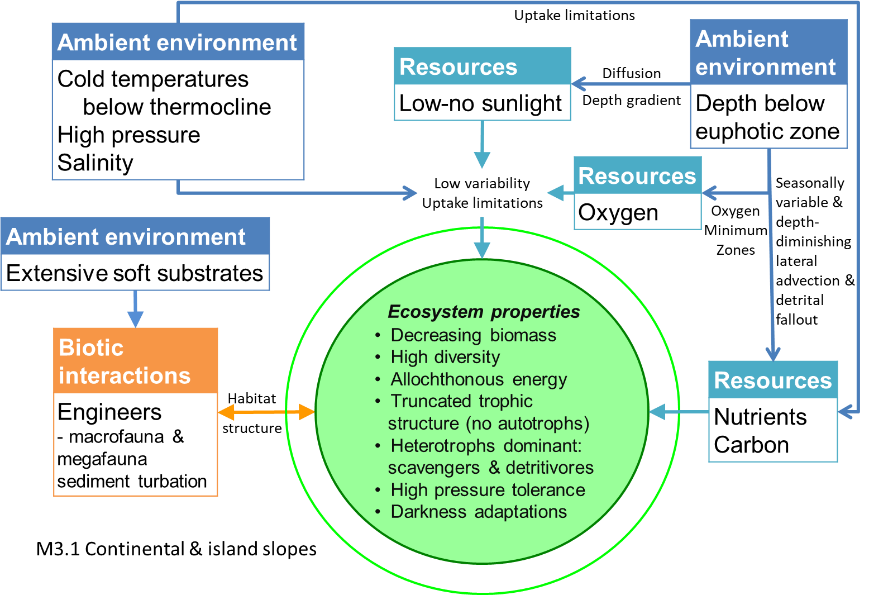
These lightless slopes of sand, mud and rocky outrops run down from the shallower shelf break to the very deep abyssal basins. Nutrients falling from upper ocean layers and delivered by currents from the shelf support diverse communities of microbial decomposers, detritivores like crabs and demersal fish, and their predators, but sessile animals are rare and algae are absent. Biomass is relatively low and peaks at mid-slope, diminishing with depth as food and temperature decrease and bathymetric pressure increases.
Key Features
Large sedimentary, aphotic, and heterotrophic slopes where depth gradients result in a bathymetric faunal zonation of high taxonomic diverstiy..
Overview of distribution
Continental slopes from shelf break (~250 m) to abyssal basins (4000 m).
Profile versions
- v1.0 (2020-01-20): E Ramirez-Llodra; UC Fernandez-Arcaya; DA Keith
- v2.0 (2020-05-28): E Ramirez-Llodra; UC Fernandez-Arcaya; IG Priede; DA Keith
- v2.01 ():
- v2.1 (2022-04-06): E Ramirez-Llodra; UC Fernandez-Arcaya; IG Priede; DA Keith Full profile available at official site
Main references
Selected references for this functional group:
Menot L, Sibuet M, Carney RS, Levin LA, Rowe GT, Billett DSM et al. (2010) New perceptions of continental margin biodiversity Life in the world’s oceans: diversity, distribution and abundance Chapter 5, pp 79-101. Blackwell, Chichester. DOI:10.1002/9781444325508.ch5
Diagrammatic assembly model
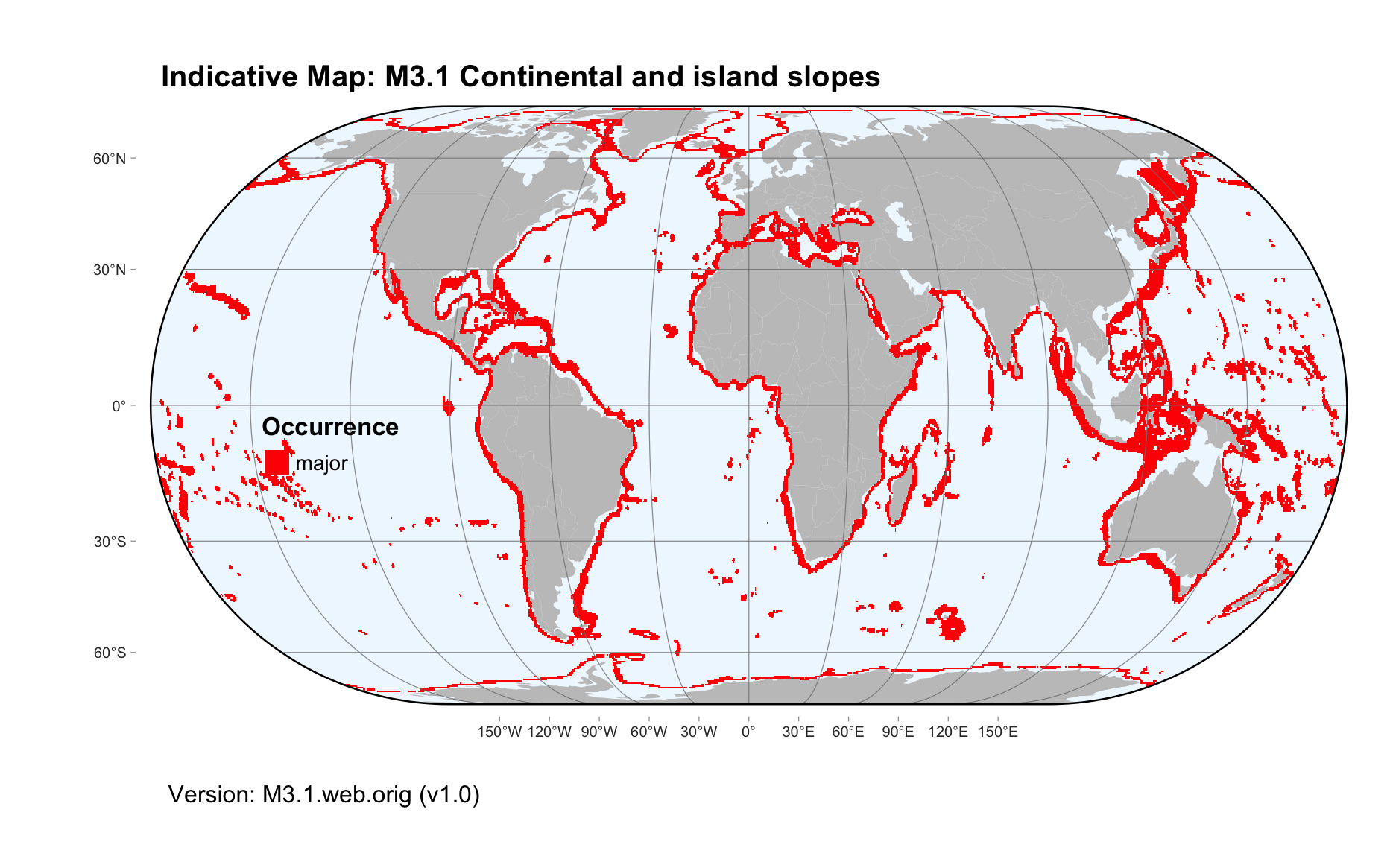
Maps
Maps are indicative of global distribution patterns are not intended to represent fine-scale patterns. The maps show areas of the world containing major (coloured red) or minor occurrences (coloured yellow) of each ecosystem functional group. See general notes on maps.
There are 2 alternative versions of the indicative map for this functional group, please compare description and sources below.
M3.1.IM.orig_v1.0
Datasets
- GSFM-2014
Map references
Harris PT, Macmillan-Lawler M, Rupp J, Baker EK (2014) Geomorphology of the oceans. Marine Geology 352: 4-24. 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.01.011
M3.1.web.orig_v1.0
Datasets
- GSFM-2014
Map references
Harris PT, Macmillan-Lawler M, Rupp J, Baker EK (2014) Geomorphology of the oceans. Marine Geology 352: 4-24. 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.01.011
Check: the Glossary / Profile structure / the public document