Global ecosystem typology
Alternative site for the Global ecosystem typology with additional information for ecosystem profiles and indicative maps.
This site is maintained by jrfep
M3.7 Chemosynthetic-based-ecosystems (CBE)
Biome: M3. Deep sea floors biome
Contributors:
(texts)
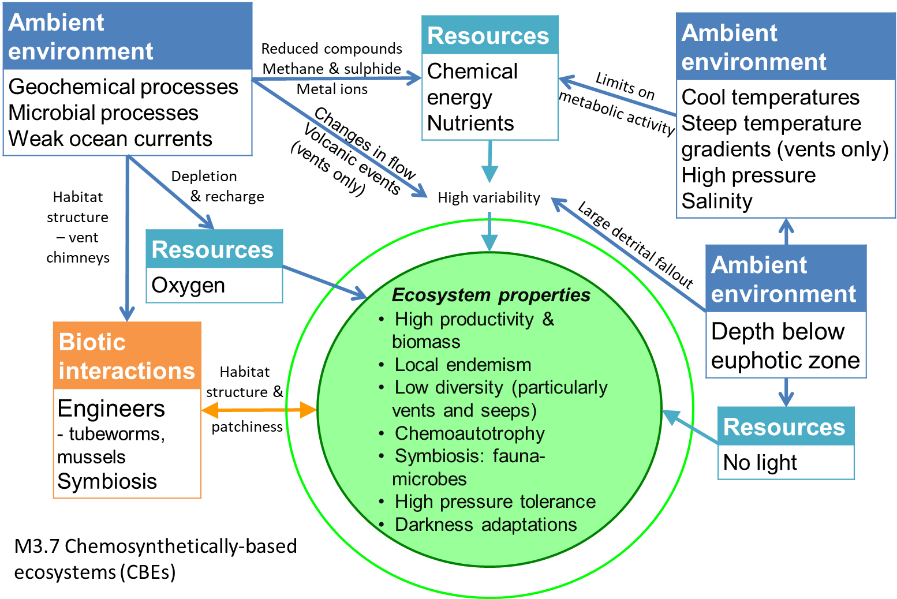
In these very deep, high pressure ecosystems, primary productivity is fuelled by chemical compounds as energy sources instead of light (chemoautotrophy). This group of productive deep sea ecosystems include: 1) hydrothermal vents on mid-ocean ridges and volcanically active seamounts, where temperatures may reach 400°C; 2) cold seeps typically on continental slopes; and 3) large organic falls of whales or wood. These specialised environments have high biomass but low diversity of organisms including microbes, tubeworms and shrimps, many of which are locally unique.
Key Features
Systems supported by microbial chemoautotrophy with high biomass of relatively low diversity, highly speciliased, fauna.
Overview of distribution
Hydrothermal vents, cold seeps, large organic falls on the deep seafloor.
Profile versions
- v1.0 (2020-01-20): E Ramirez-Llodra; DA Keith
- v2.0 (2020-05-31): E Ramirez-Llodra; DA Keith
- v2.01 ():
- v2.1 (2022-04-06): E Ramirez-Llodra; UC Fernandez-Arcaya; S Rossi; DA Keith Full profile available at official site
Main references
Selected references for this functional group:
Tunnicliffe V, Juniper KS, Sibuet M (2003) Reducing environments of the deep-sea floor Ecosystems of the World Vol 28 Ecosystems of the deep oceans, pp 81-110. Elsevier, London.
Diagrammatic assembly model
Maps
Maps are indicative of global distribution patterns are not intended to represent fine-scale patterns. The maps show areas of the world containing major (coloured red) or minor occurrences (coloured yellow) of each ecosystem functional group. See general notes on maps.
There are 2 alternative versions of the indicative map for this functional group, please compare description and sources below.
M3.7.IM.orig_v1.0
Datasets
- ESRI-plate-tectonics
Map references
M3.7.web.orig_v1.0
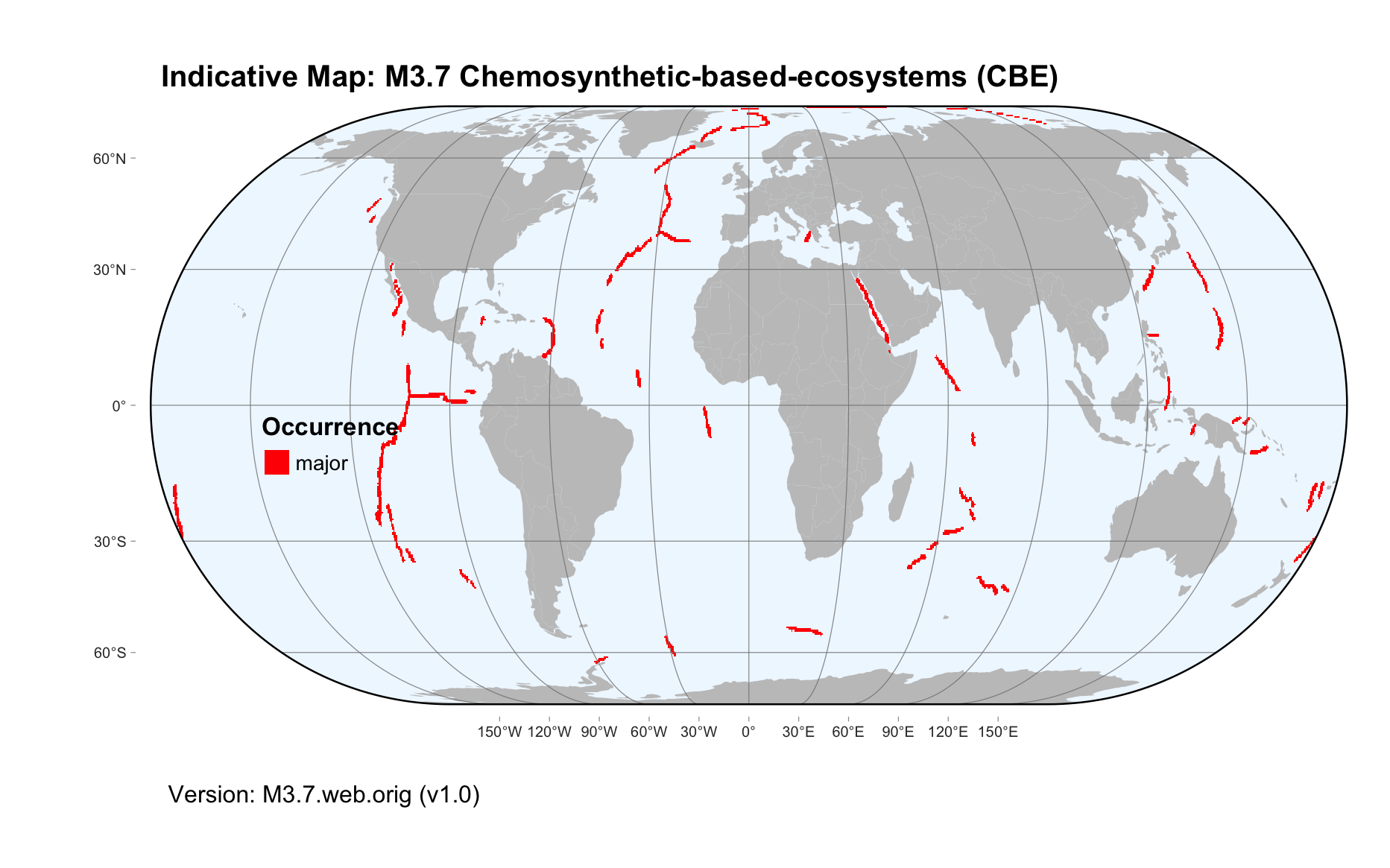
Datasets
- ESRI-plate-tectonics
Map references
Check: the Glossary / Profile structure / the public document