Global ecosystem typology
Alternative site for the Global ecosystem typology with additional information for ecosystem profiles and indicative maps.
This site is maintained by jrfep
MT1.1 Rocky Shorelines
Biome: MT1. Shorelines biome
Contributors:
(texts)
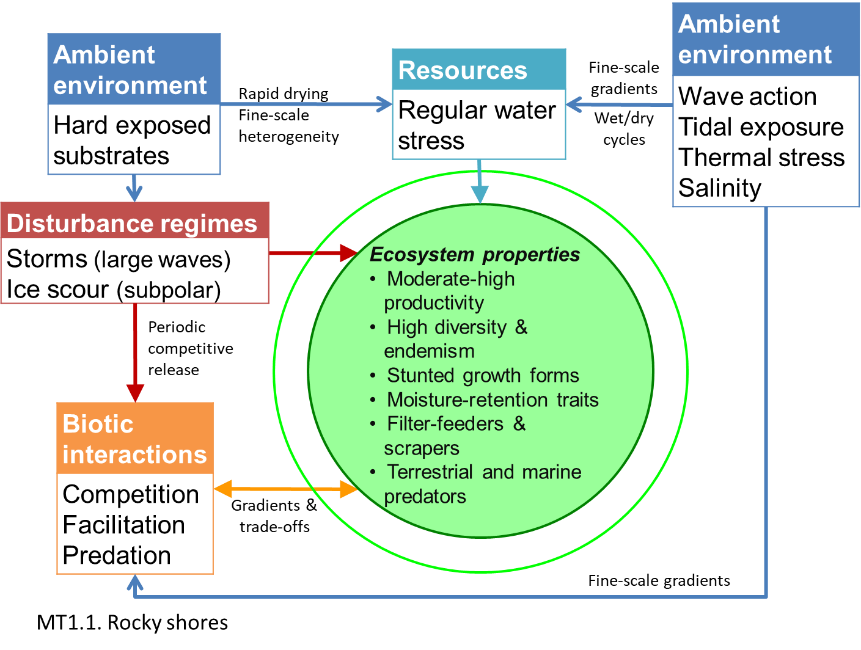
Waves, tides and a gradient of exposure drive the structure and function of these productive intertidal ecosystems found mostly on high energy coasts. The biota includes filter feeders like barnacles, mussels and sea squirts which compete for limited space. Grazers like limpets and urchins consume small sessile algae, while predators such as crabs, fish and birds consume a wide range of prey. Organisms use microhabitats during low tide (e.g. rockpools, crevices) or have adaptations like shells to survive exposure to high temperatures, salinity and desiccation.
Key Features
Hard intertidal substrate, dominated by sessile and mobile invertebrates, and macroalgae.
Overview of distribution
High-energy shorelines globally.
Profile versions
- v1.0 (2020-01-20): MJ Bishop; DA Keith
- v2.0 (2020-05-28): MJ Bishop; LB Firth; SL McSweeney; TP Crowe; AH Altieri; DA Keith
- v2.01 ():
- v2.1 (2022-04-06): MJ Bishop; LB Firth; SL McSweeney; TP Crowe; AH Altieri; DA Keith Full profile available at official site
Main references
Selected references for this functional group:
Connell JH (1972) Community interactions on marine rocky intertidal shores Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 3:169-192 DOI:10.1146/annurev.es.03.110172.001125
Thompson RC, Crowe TP, Hawkins SJ (2002) Rocky intertidal communities: past environmental changes, present status and predictions for the next 25 years Environmental Conservation 29:168-91 DOI:10.1017/s0376892902000115
Diagrammatic assembly model
Maps
Maps are indicative of global distribution patterns are not intended to represent fine-scale patterns. The maps show areas of the world containing major (coloured red) or minor occurrences (coloured yellow) of each ecosystem functional group. See general notes on maps.
There are 2 alternative versions of the indicative map for this functional group, please compare description and sources below.
MT1.1.IM.grid_v2.0
Datasets
- MEOW-2008
Map references
Spalding MD, Fox HE, Allen GR, Davidson N, Ferdaña ZA, Finlayson M, Halpern BS, Jorge MA, Lombana A, Lourie SA, Martin KD, McManus E, Molnar J, Recchia CA, Robertson J (2007) Marine ecoregions of the world: a bioregionalization of coastal and shelf areas. Bioscience 57: 573–583. DOI:10.1641/B570707
MT1.1.web.map_v1.0
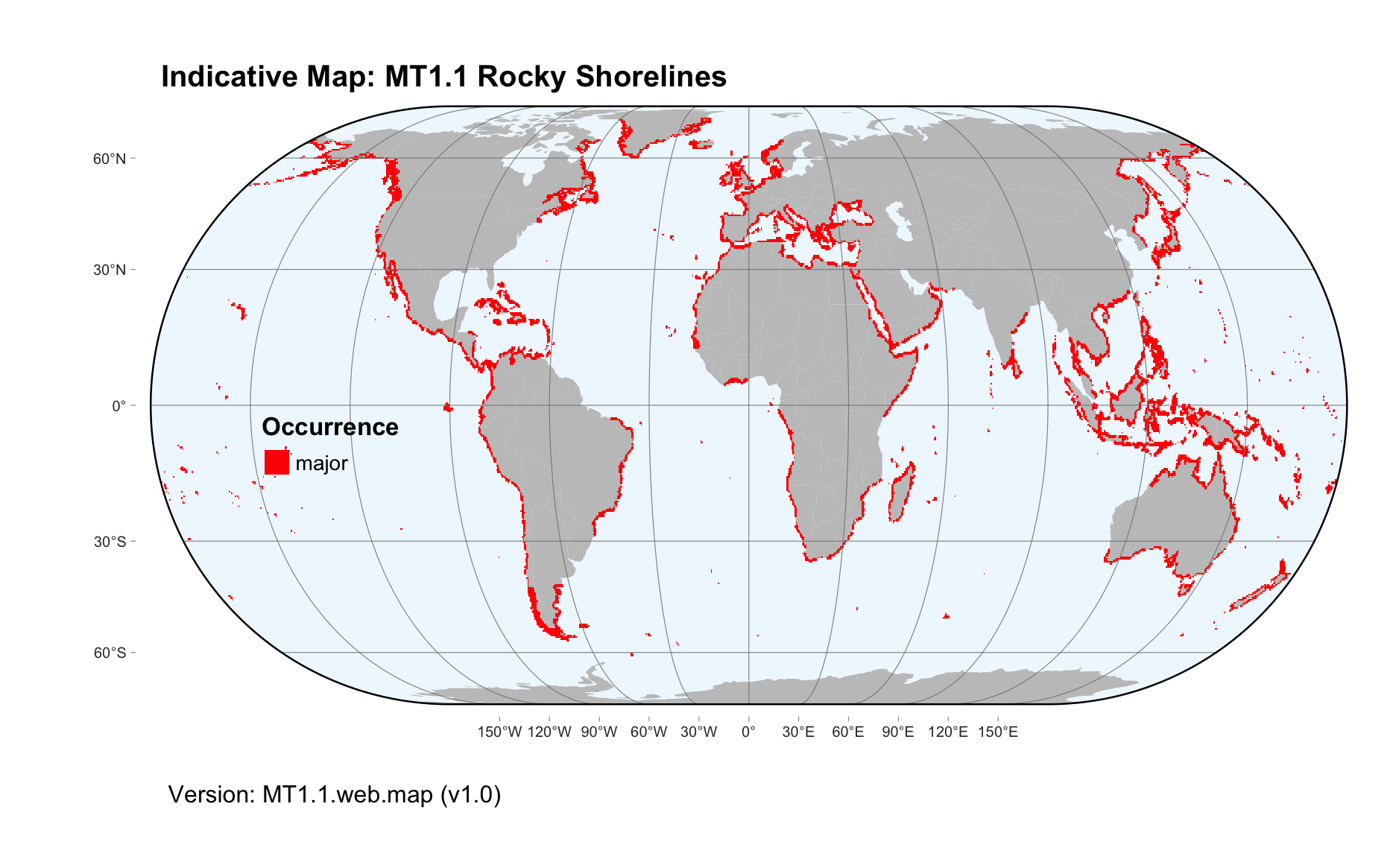
Datasets
- MEOW-2008
- GSFM-2014
Map references
Spalding MD, Fox HE, Allen GR, Davidson N, Ferdaña ZA, Finlayson M, Halpern BS, Jorge MA, Lombana A, Lourie SA, Martin KD, McManus E, Molnar J, Recchia CA, Robertson J (2007) Marine ecoregions of the world: a bioregionalization of coastal and shelf areas. Bioscience 57: 573–583. DOI:10.1641/B570707
Harris PT, Macmillan-Lawler M, Rupp J, Baker EK (2014) Geomorphology of the oceans. Marine Geology 352: 4-24. 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.01.011
Check: the Glossary / Profile structure / the public document